Table of Contents
- Mixing Interface overview
- Create and add sources
- Mixing View : control opacity
- Geometry View : place and move sources
- Layers View : bring to front or back
- Texturing View : crop, repeat and apply masks
- Transition View : smooth session loading
- Source configuration panel
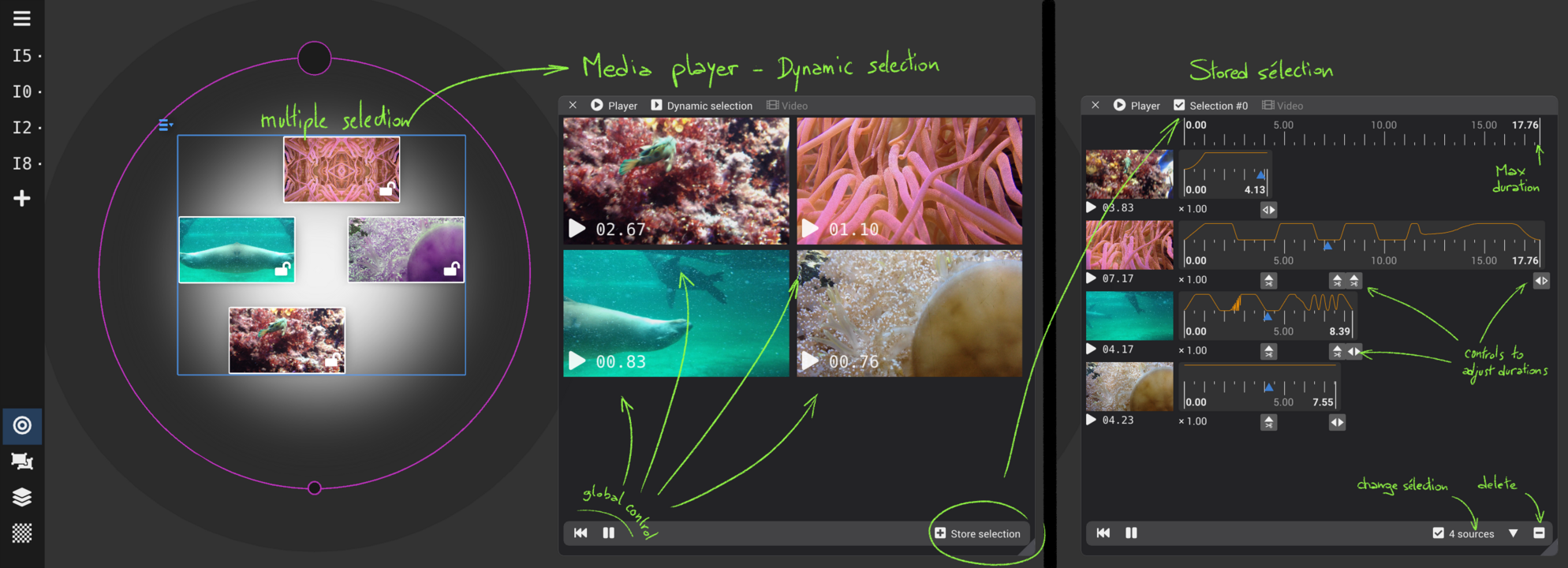
- Media player : control playback of media
- Record output stream
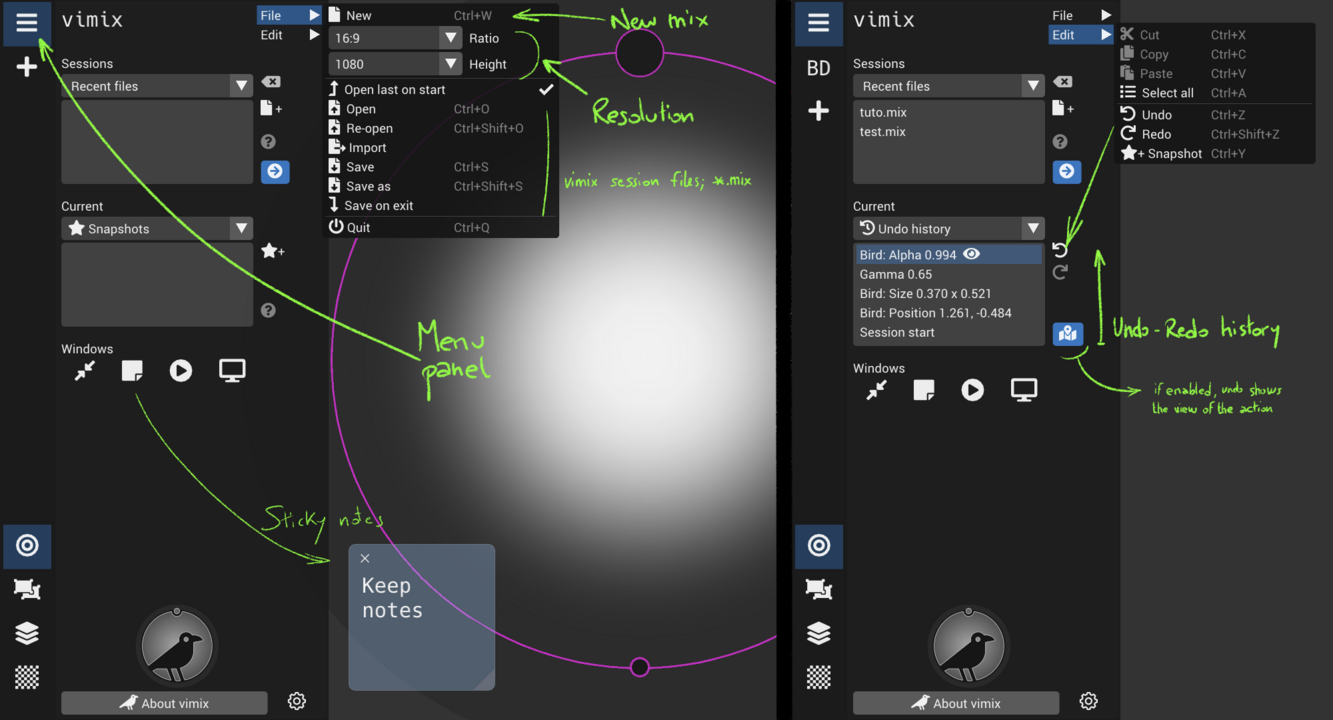
Mixing Interface overview
Application Menu
Application Settings
The 4 views
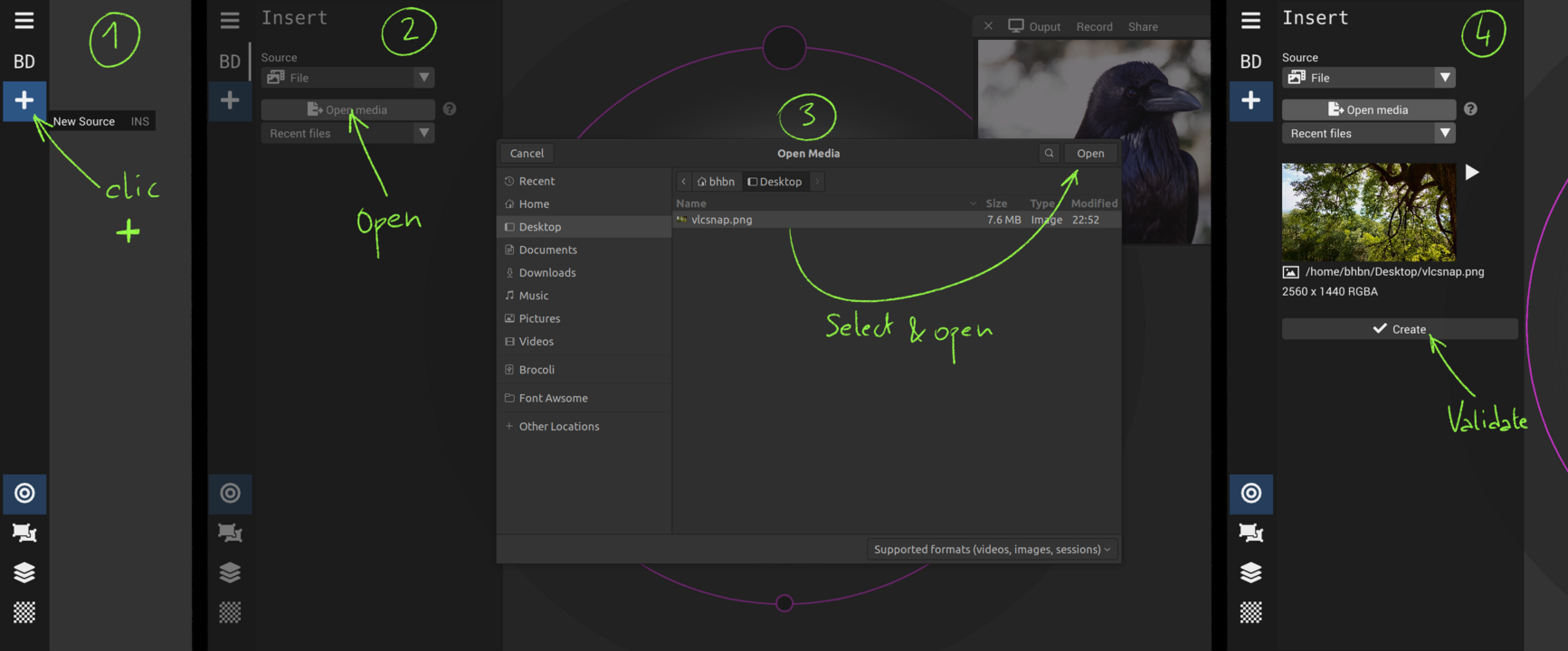
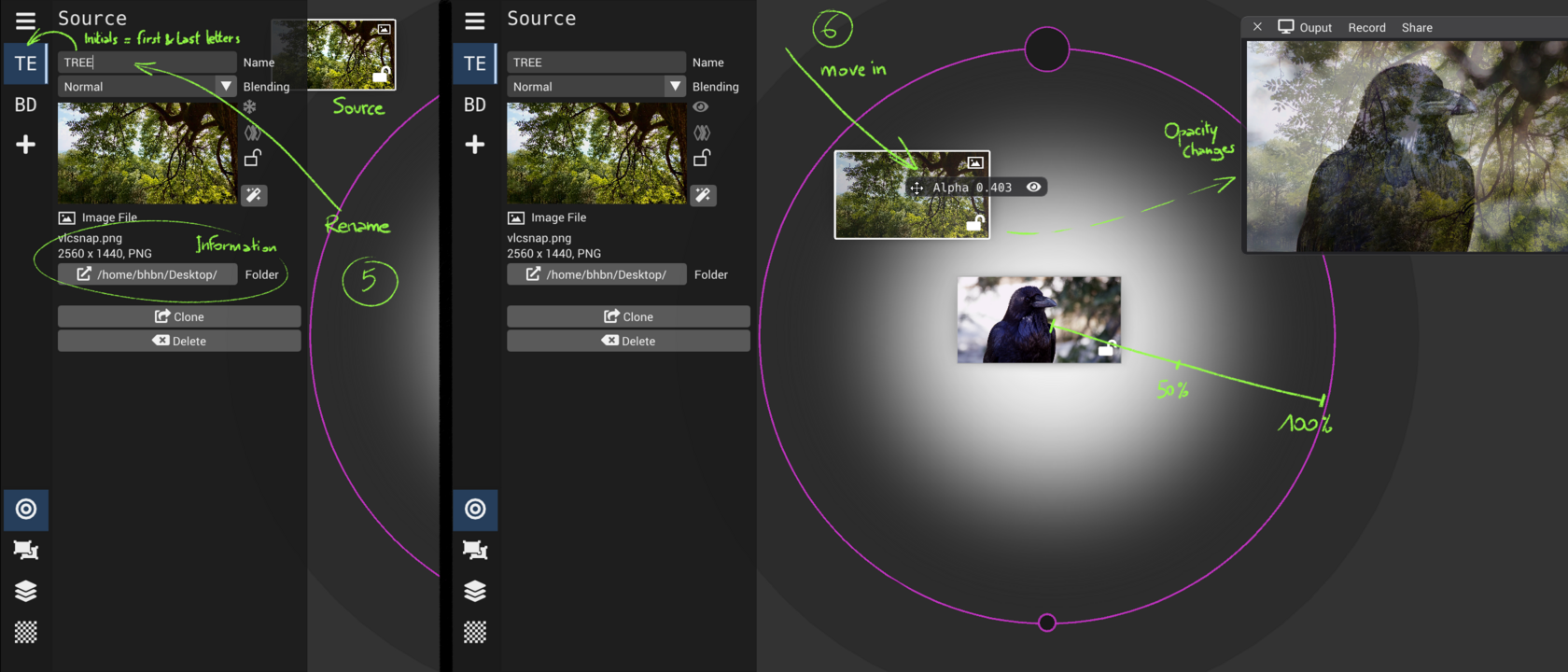
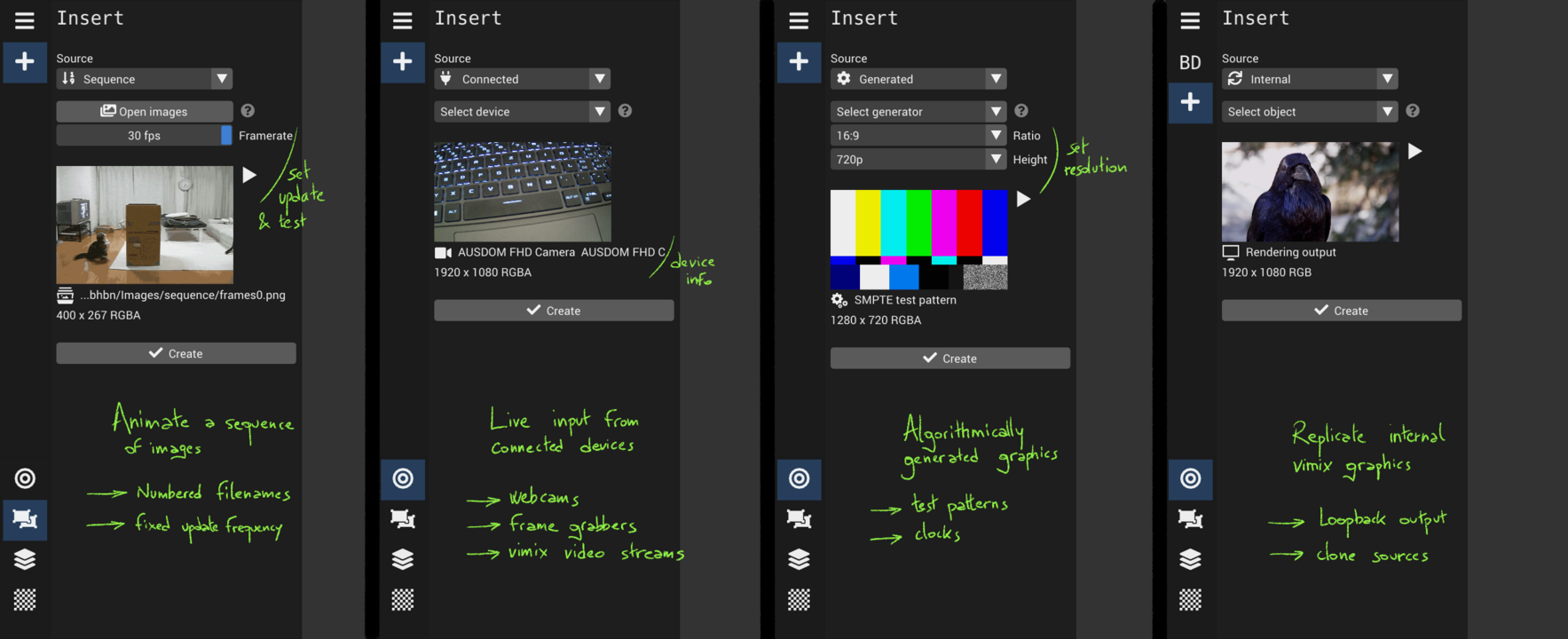
Create and add sources
Various types of sources
ℹ️ You can also create sources that connect to network video streams
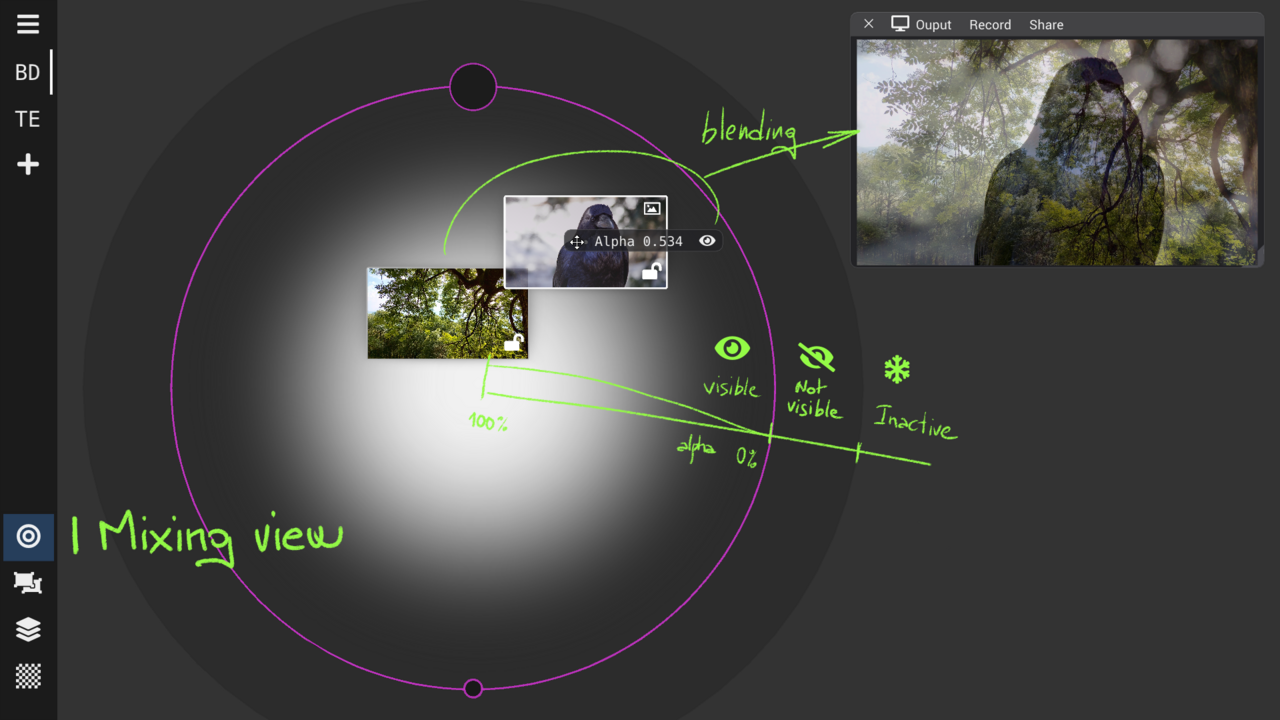
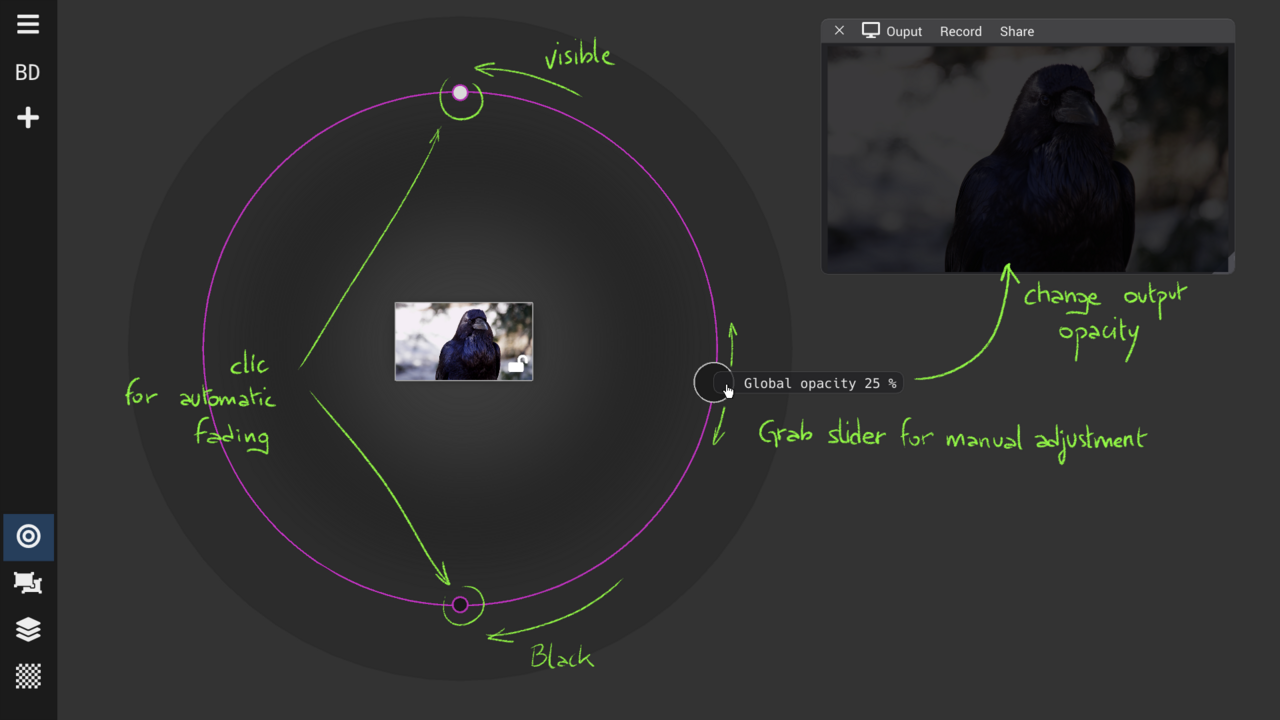
Mixing View : control opacity
Global opacity
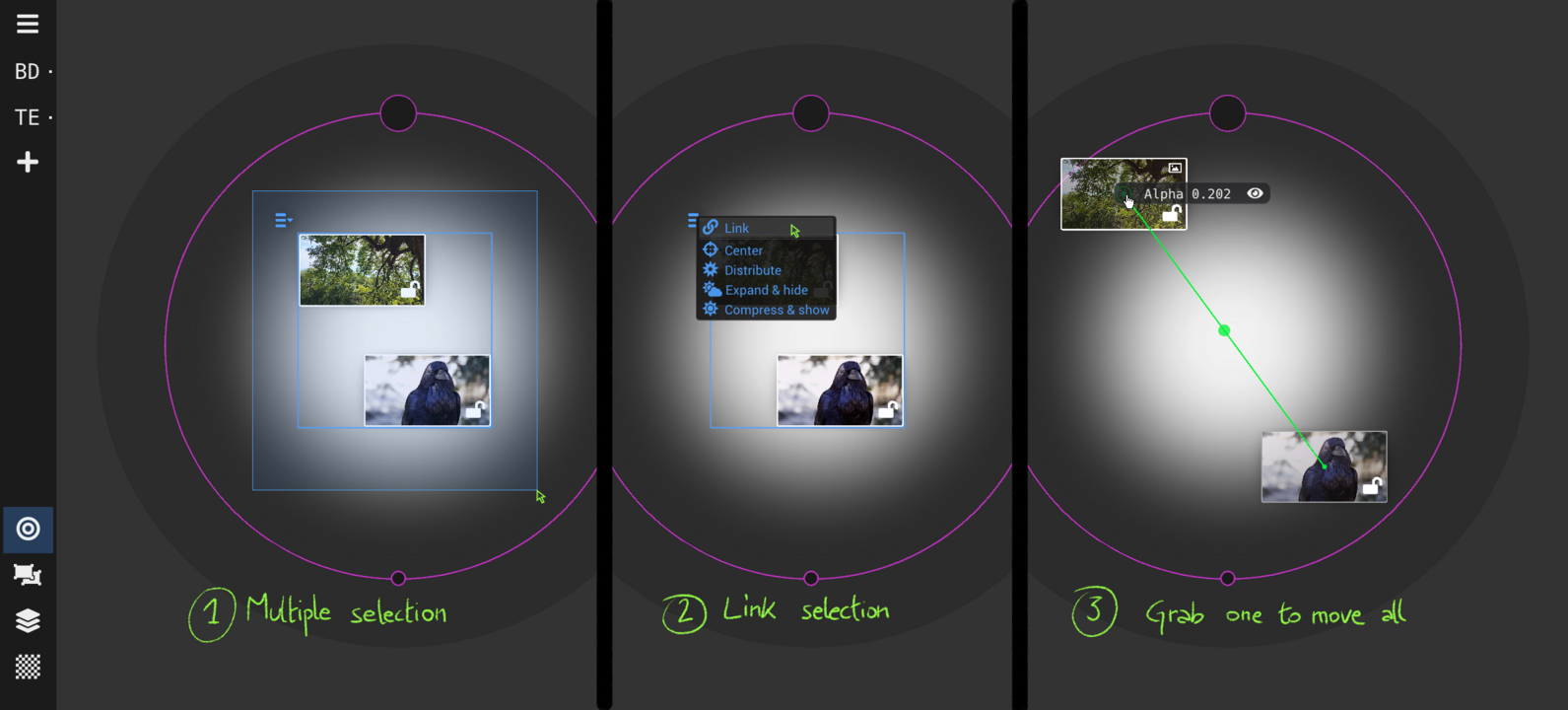
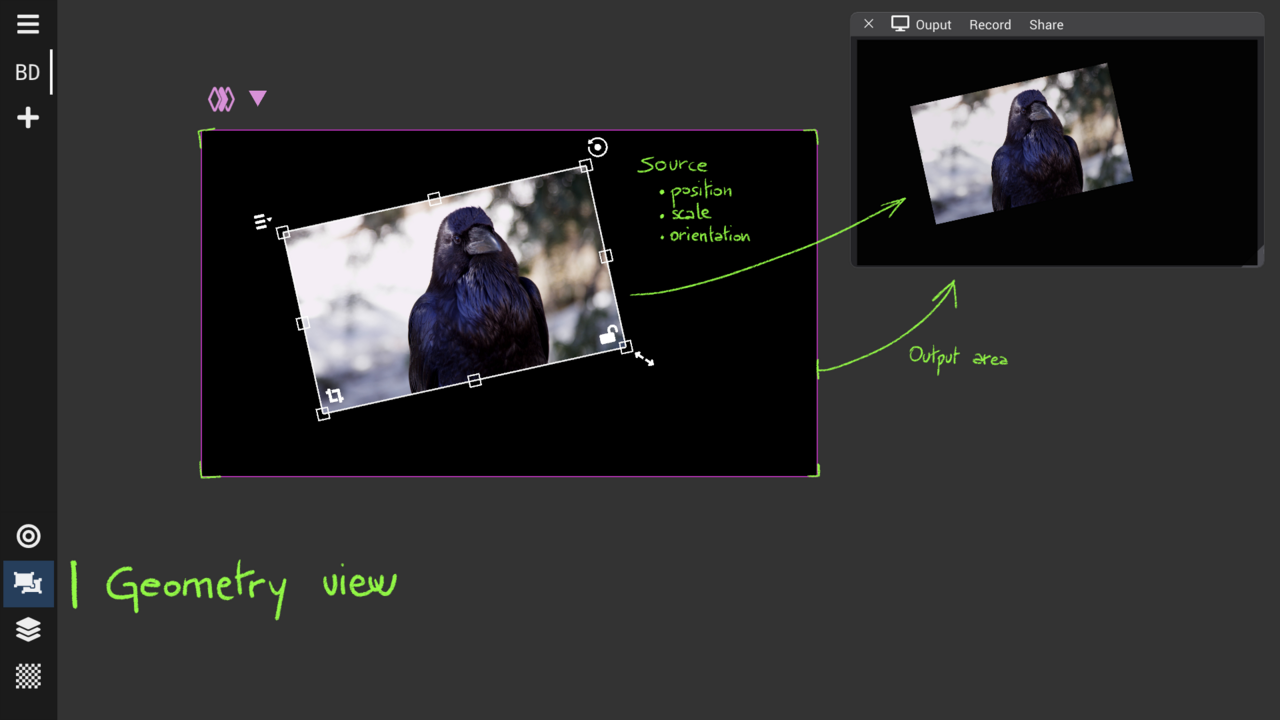
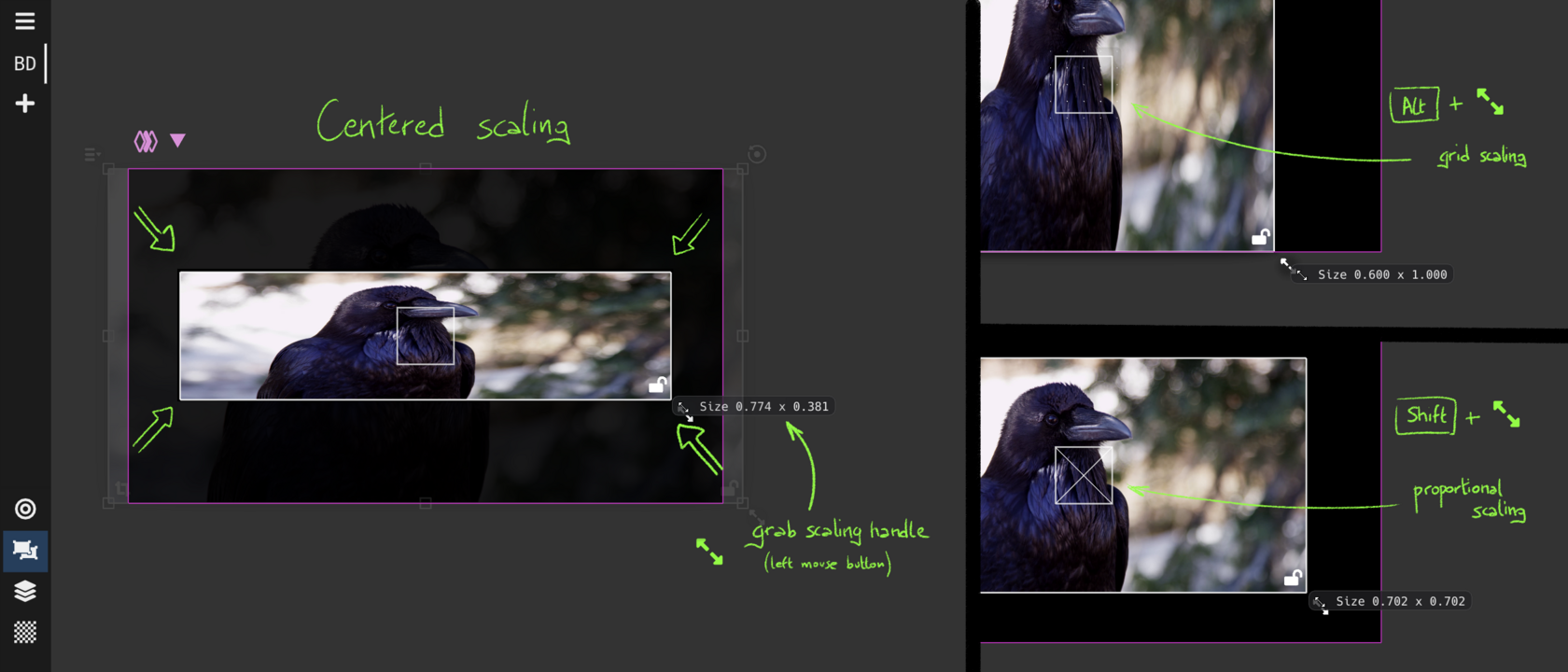
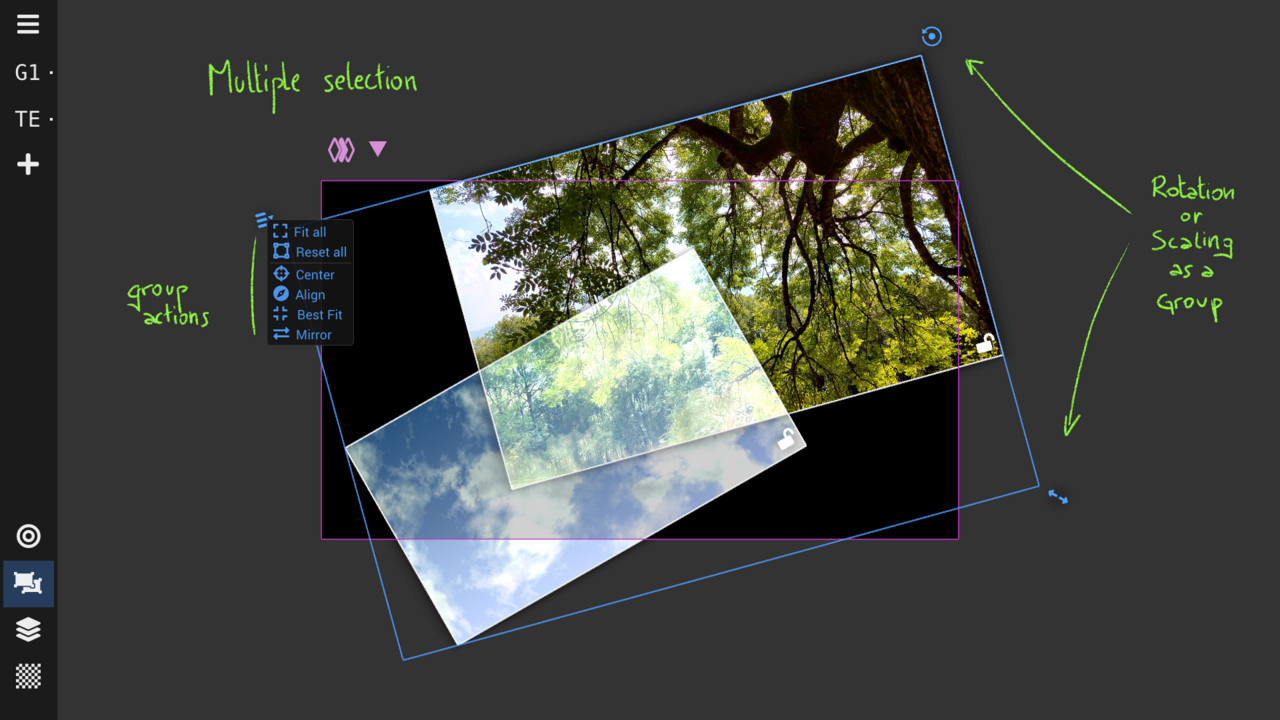
Geometry View : place and move sources
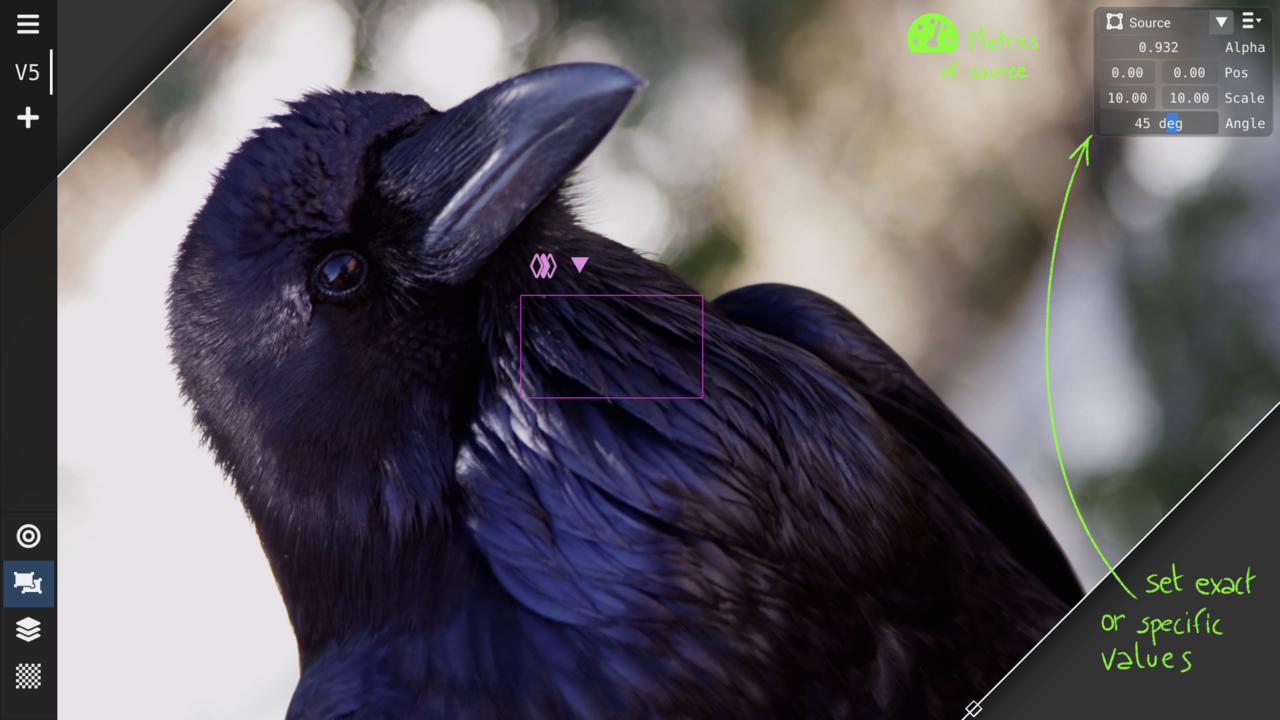
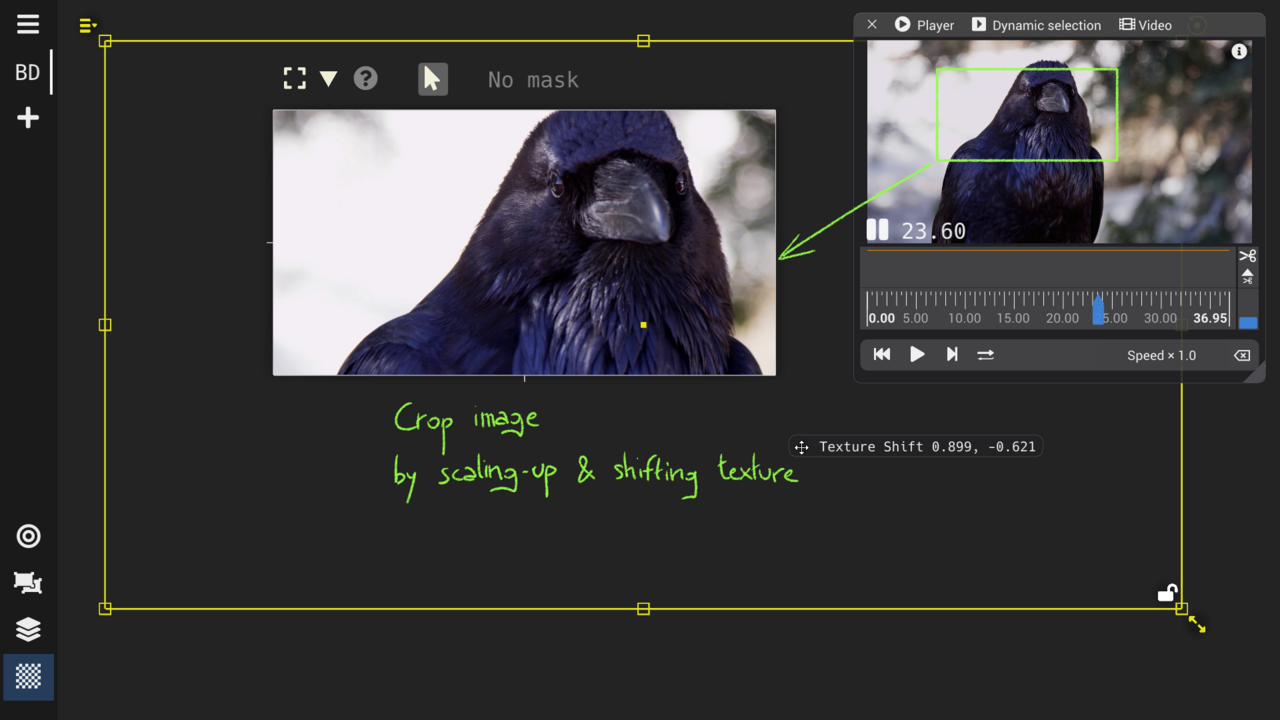
Geometric transformations: translation, scaling, rotation, and crop
Transform multiple sources as a group
Open the metrics toolbox (from Settings) to set specific values
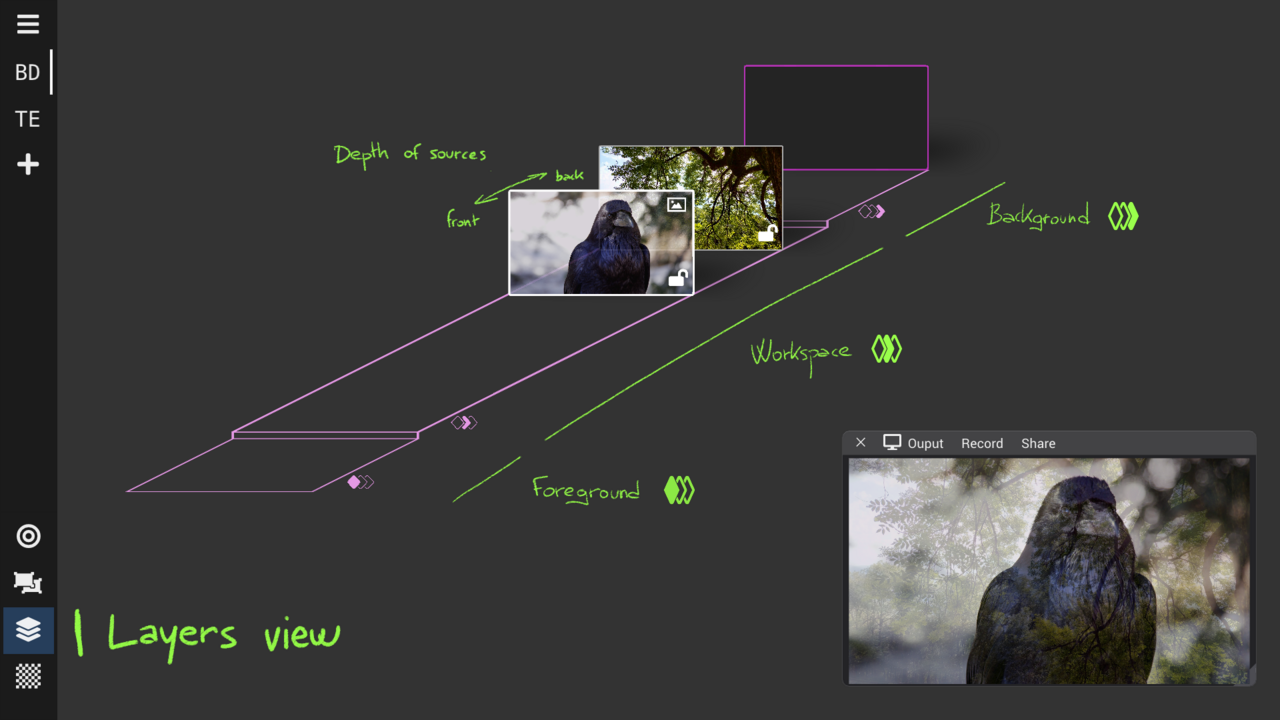
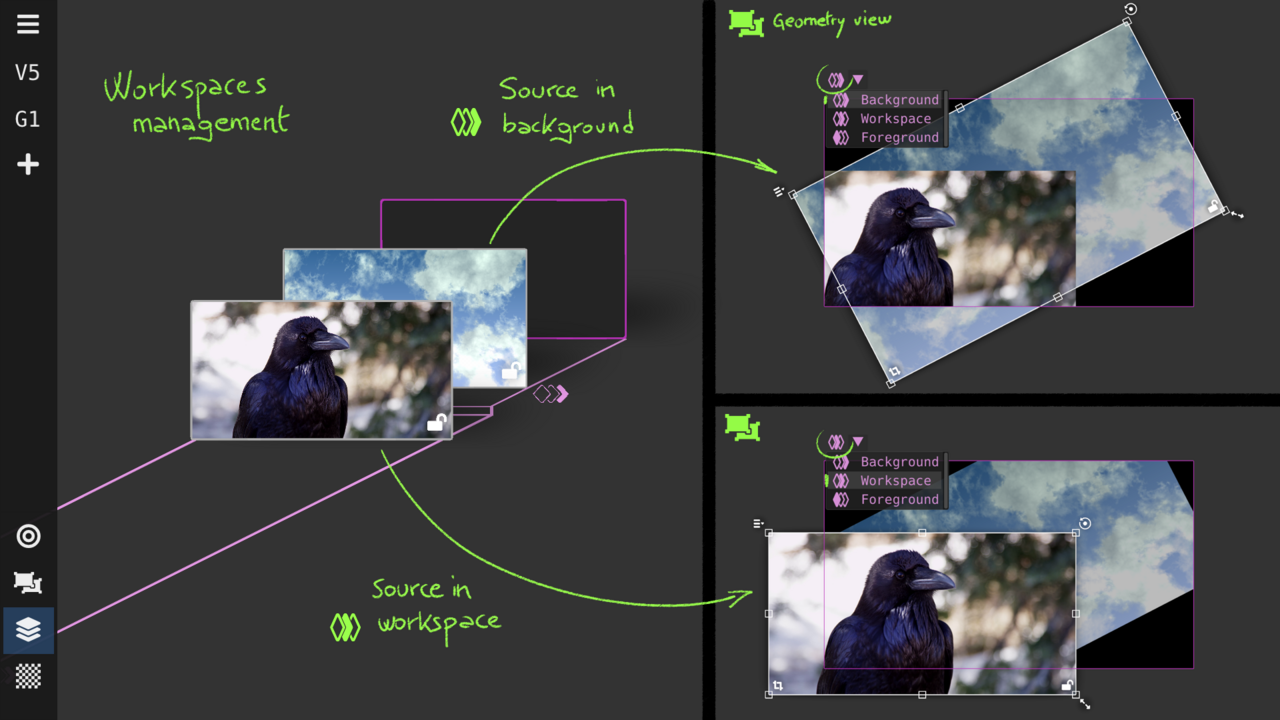
Layers View : bring to front or back
Layers define workspaces linked to the geometry view
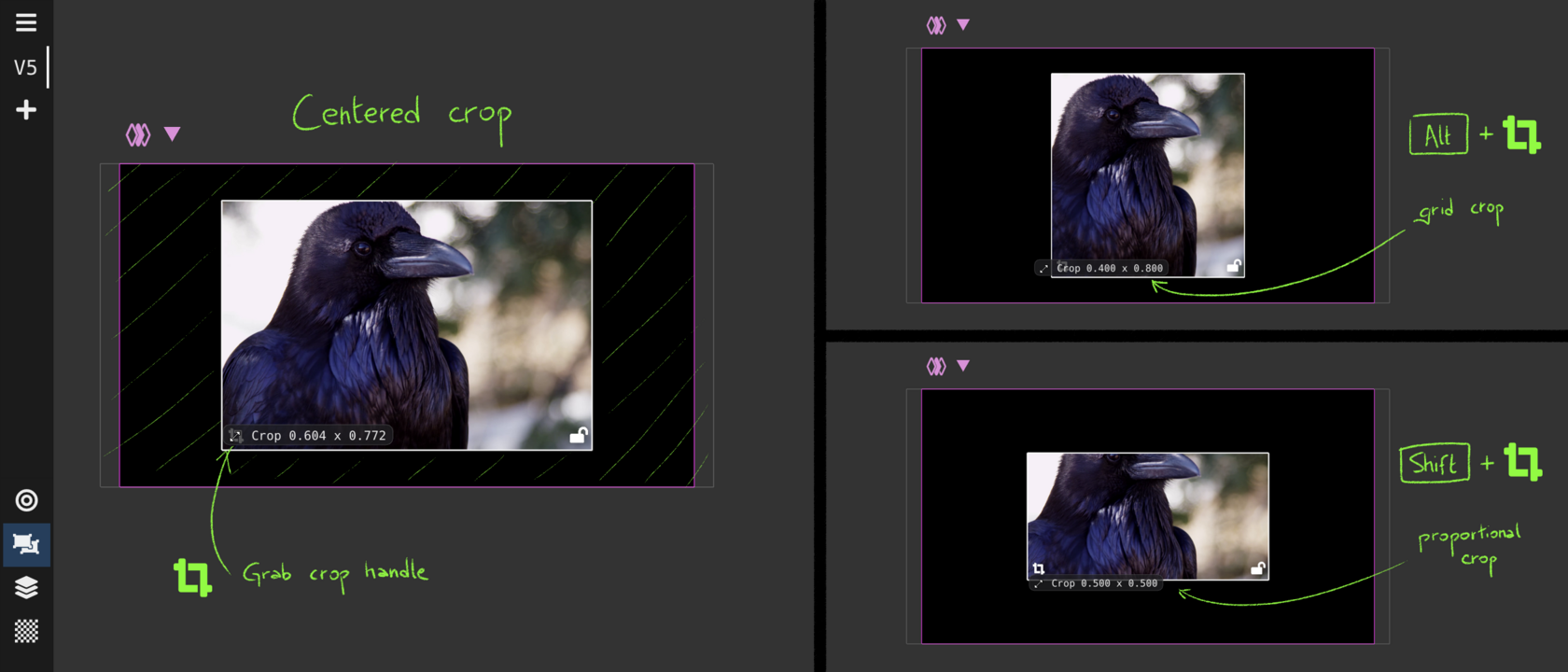
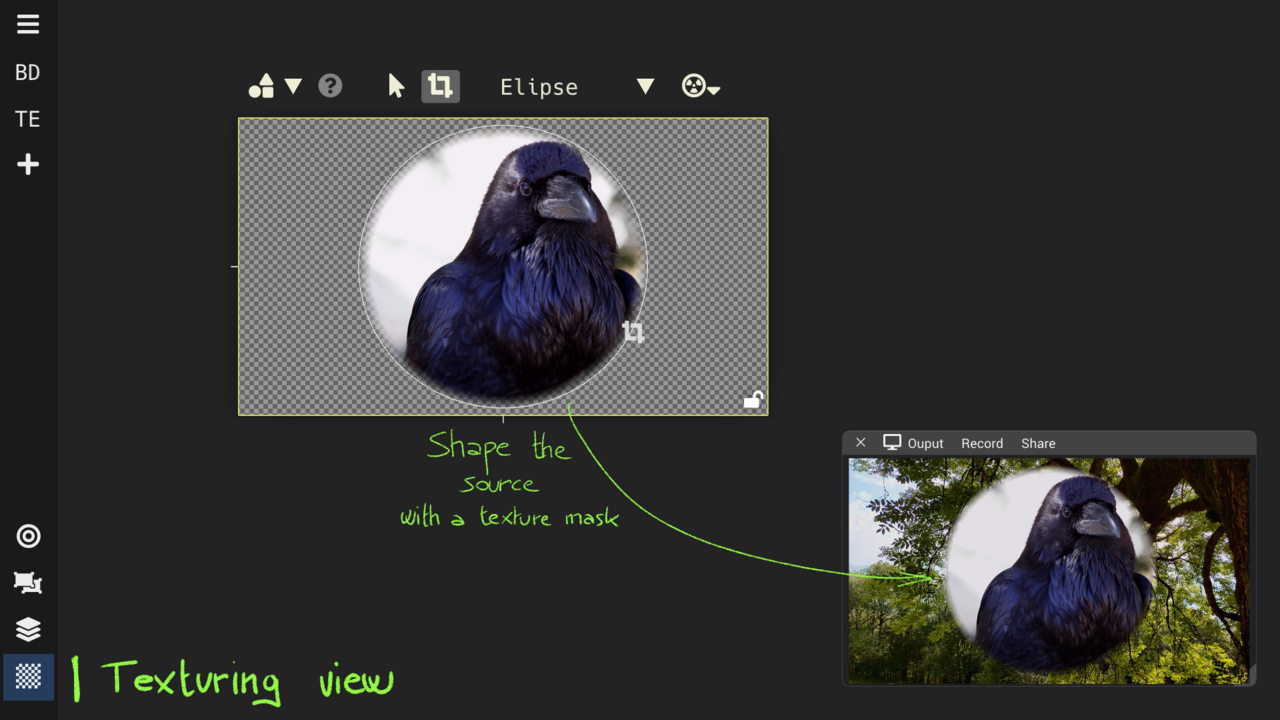
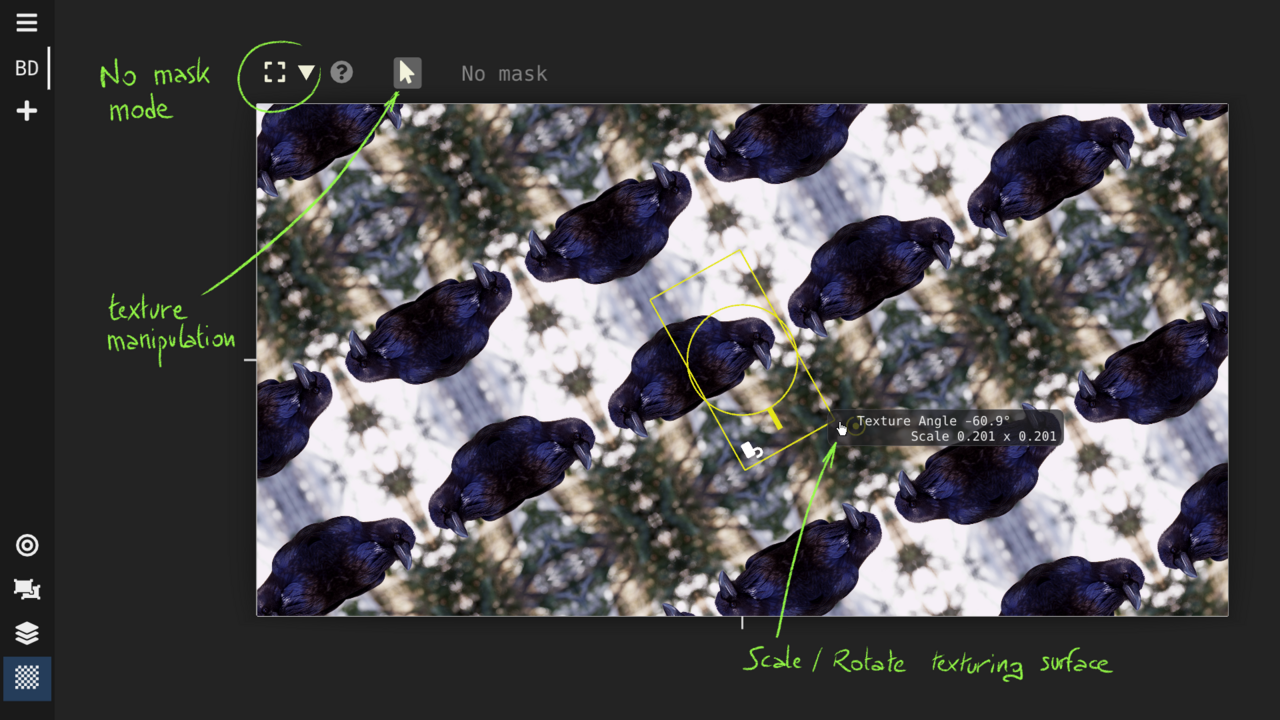
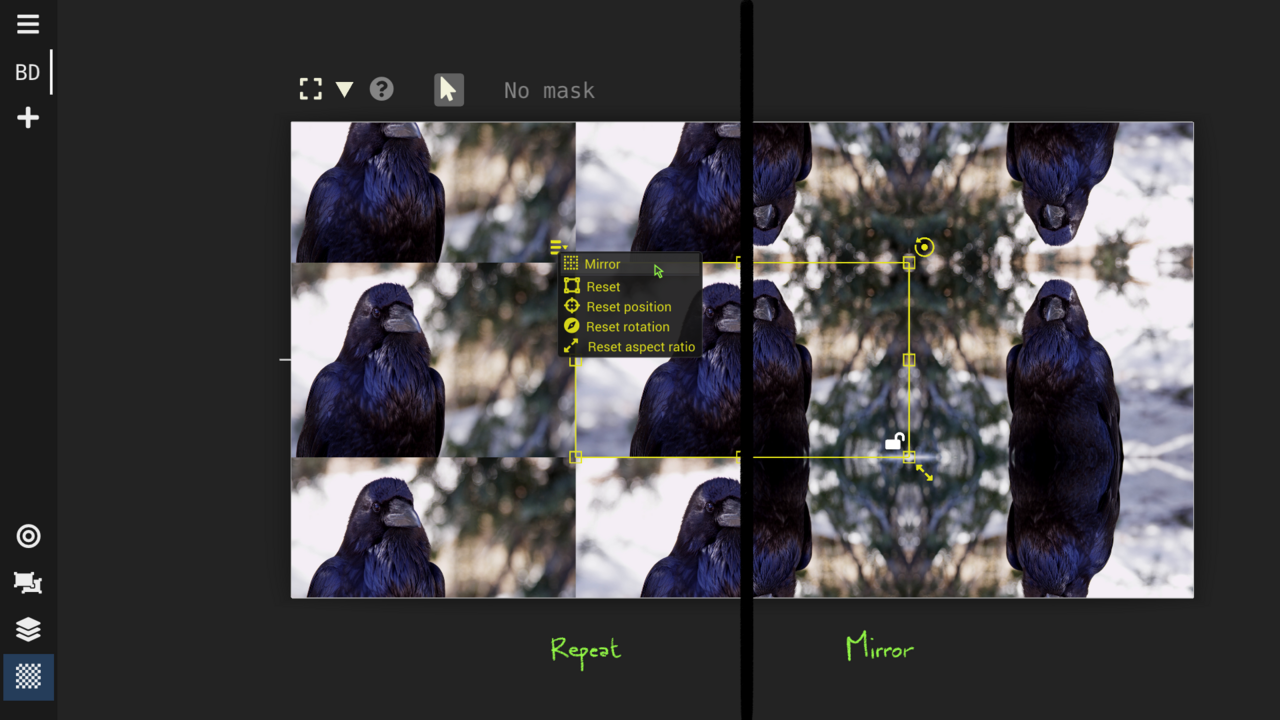
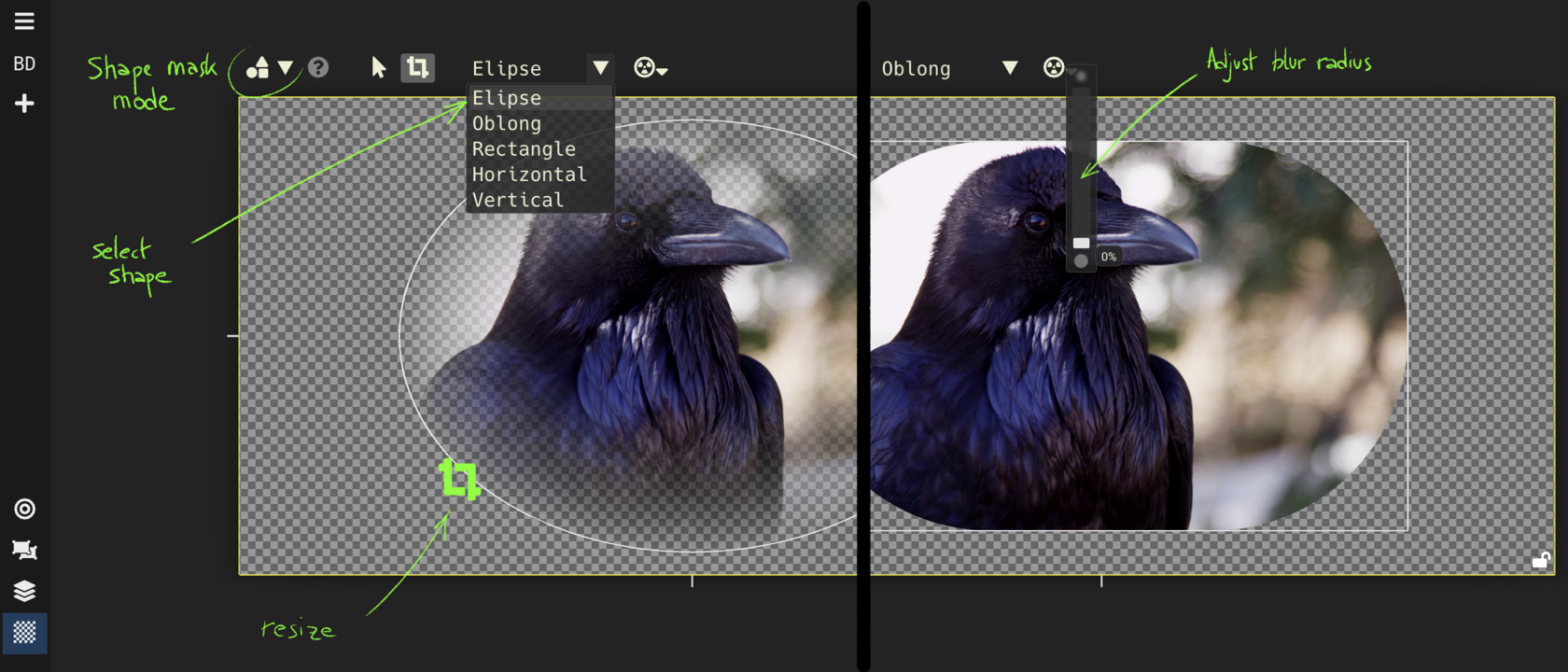
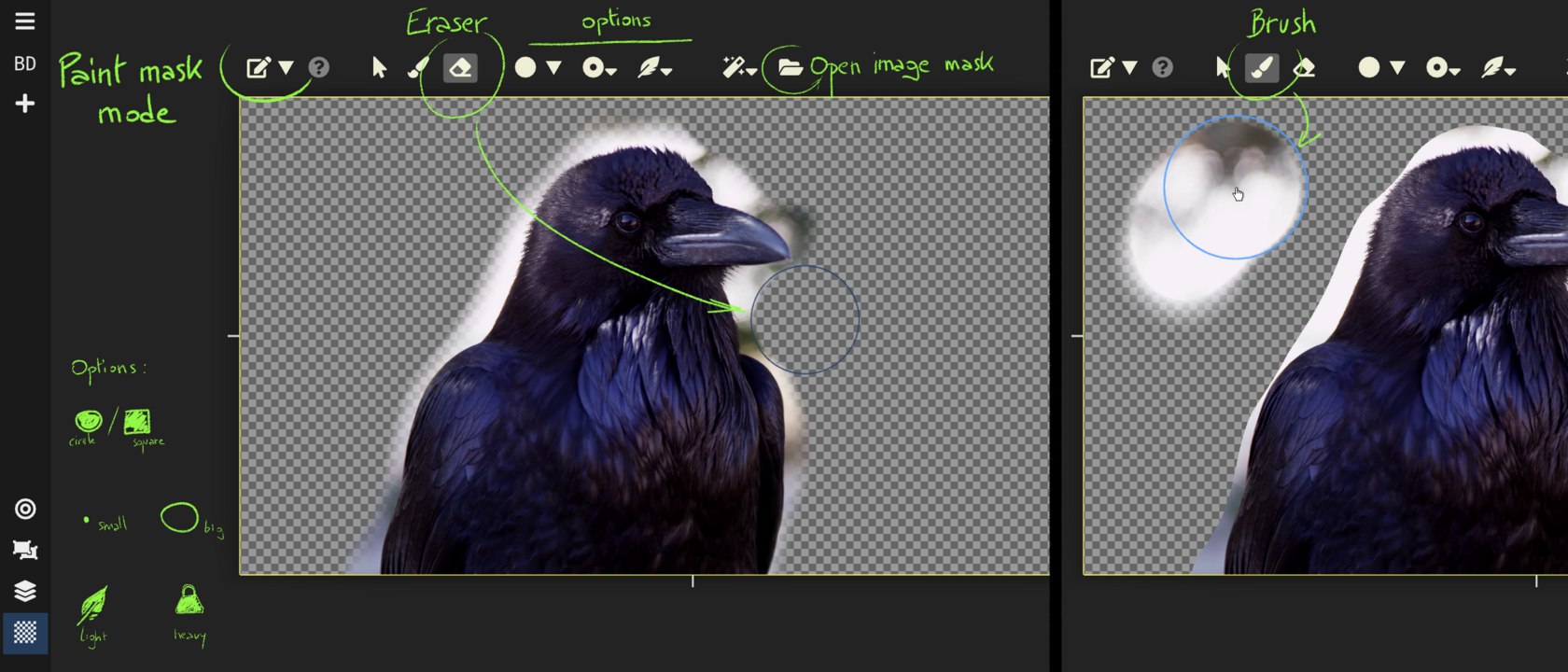
Texturing View : crop, repeat and apply masks
Add alpha mask to the texture; standard shapes or hand drawn
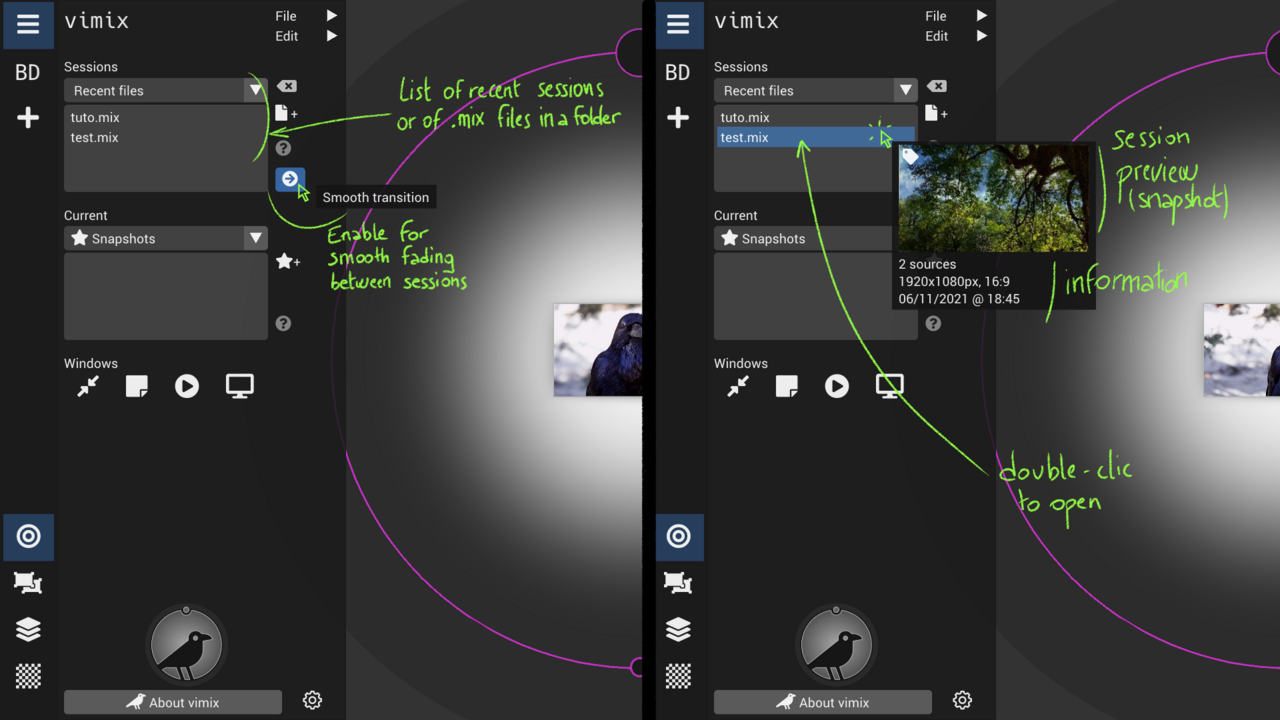
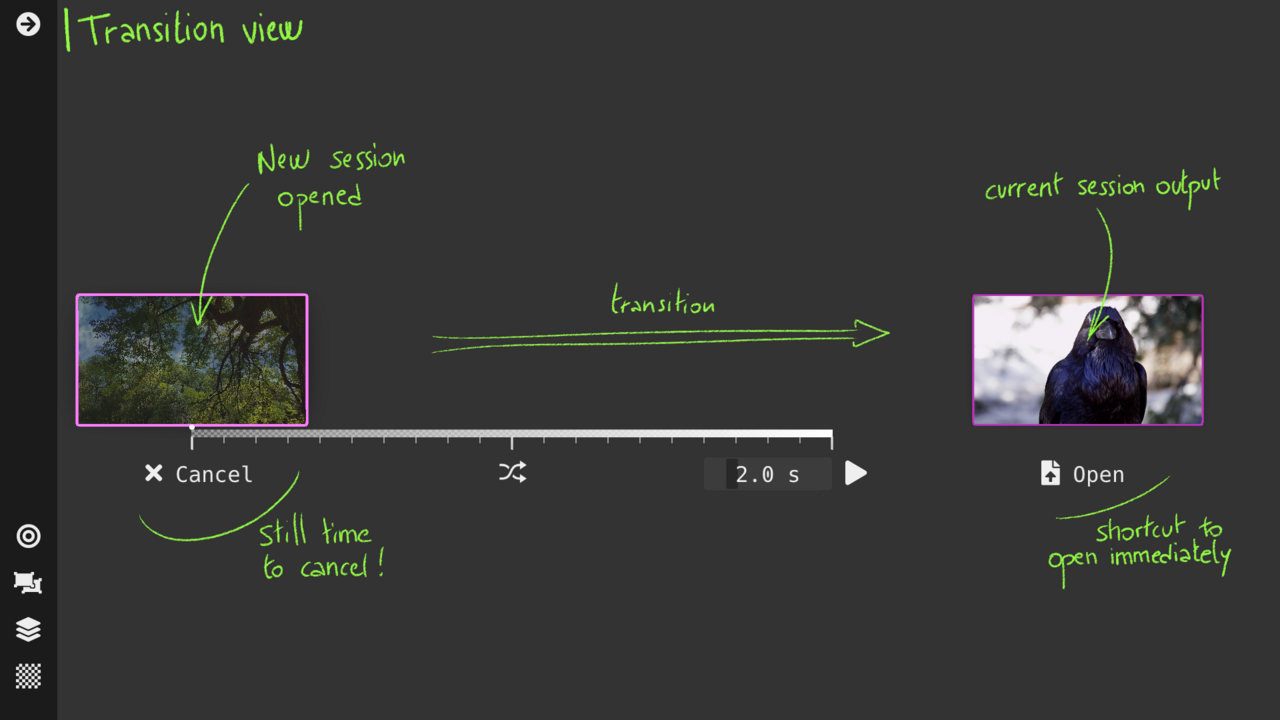
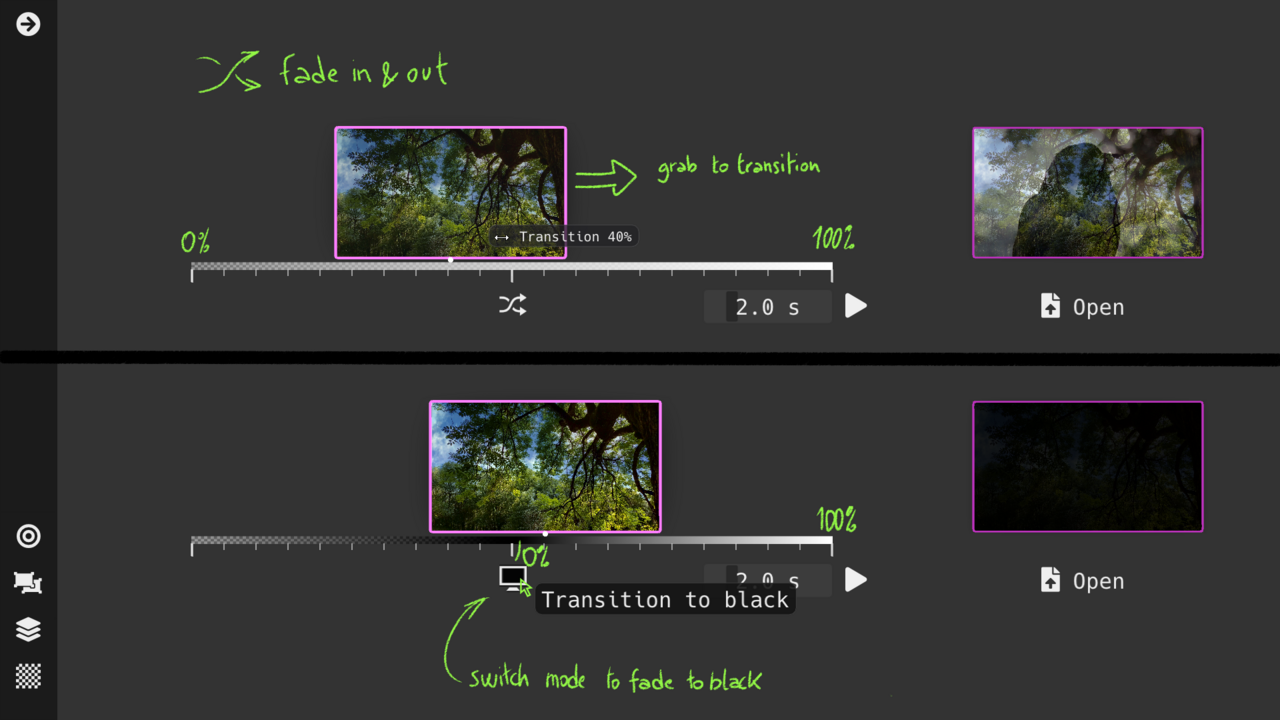
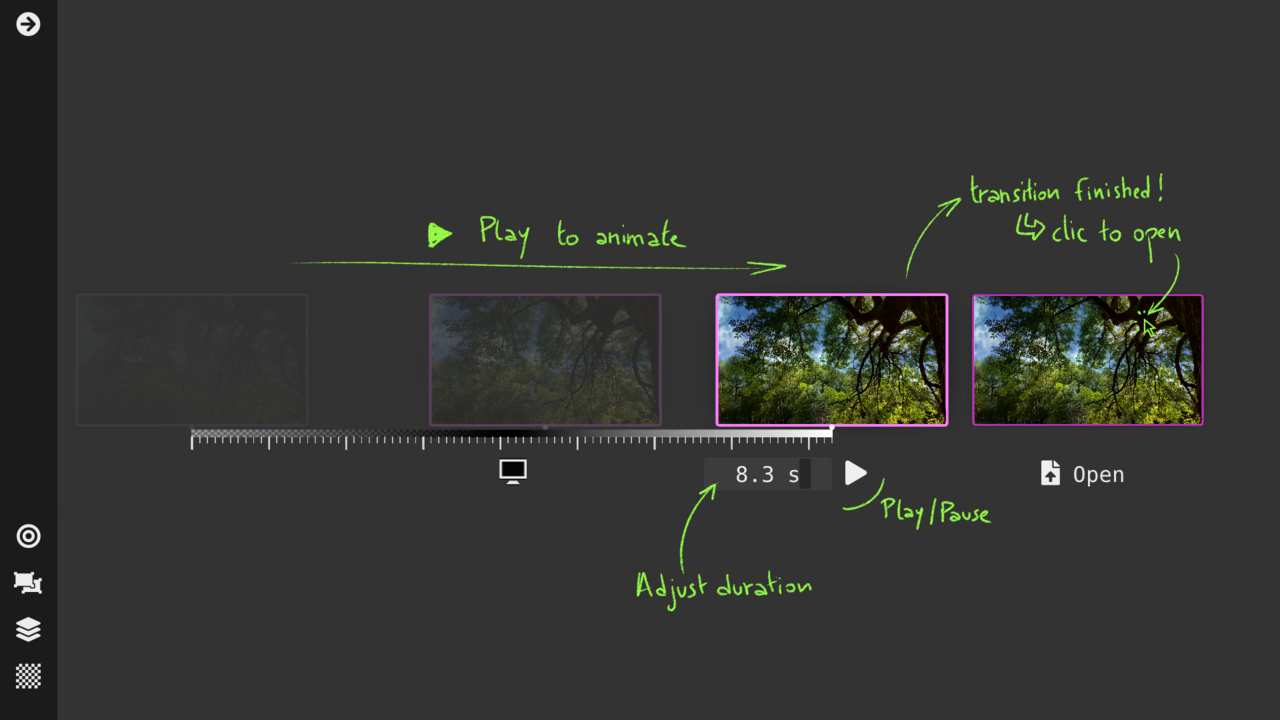
Transition View : smooth session loading
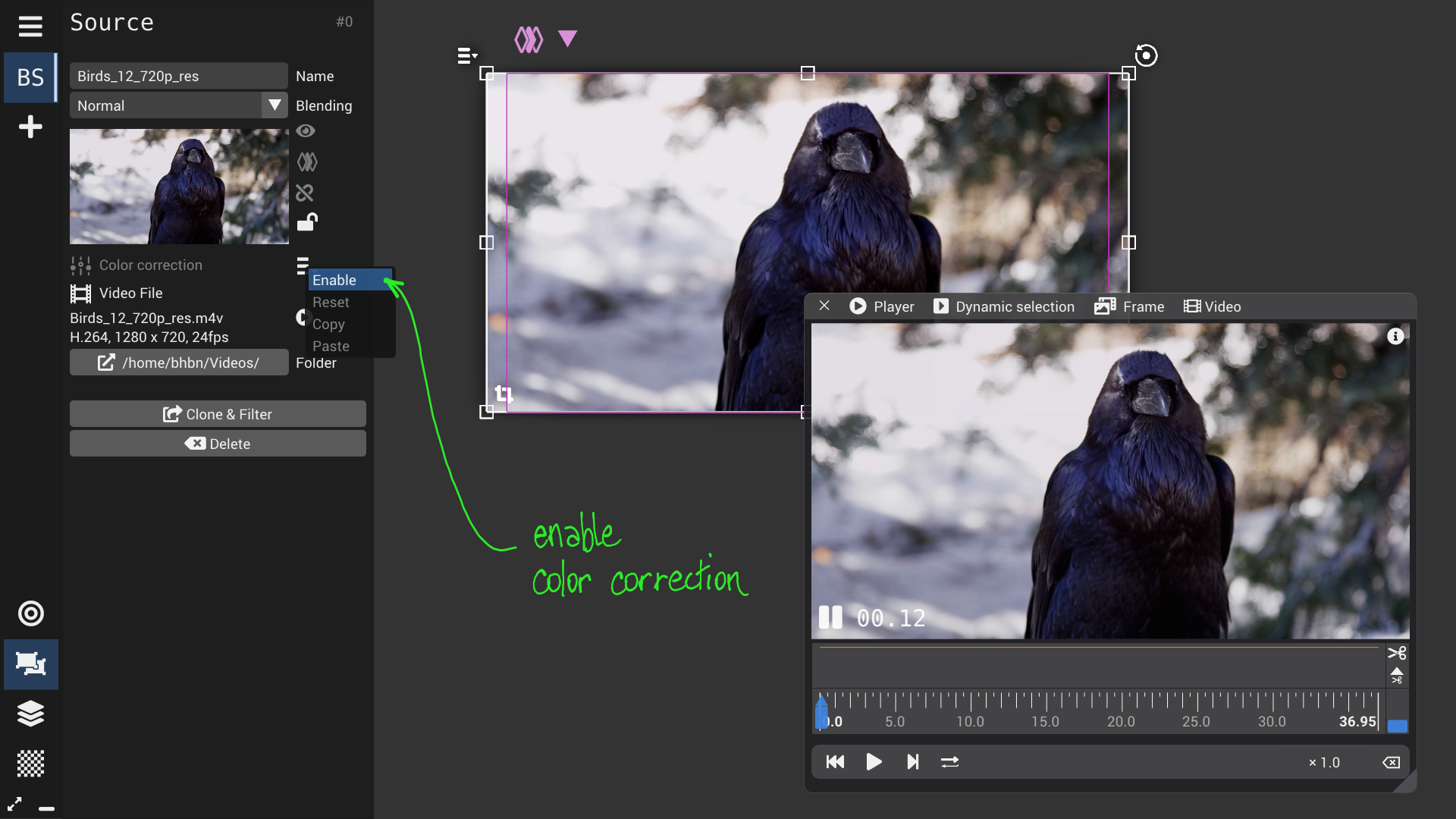
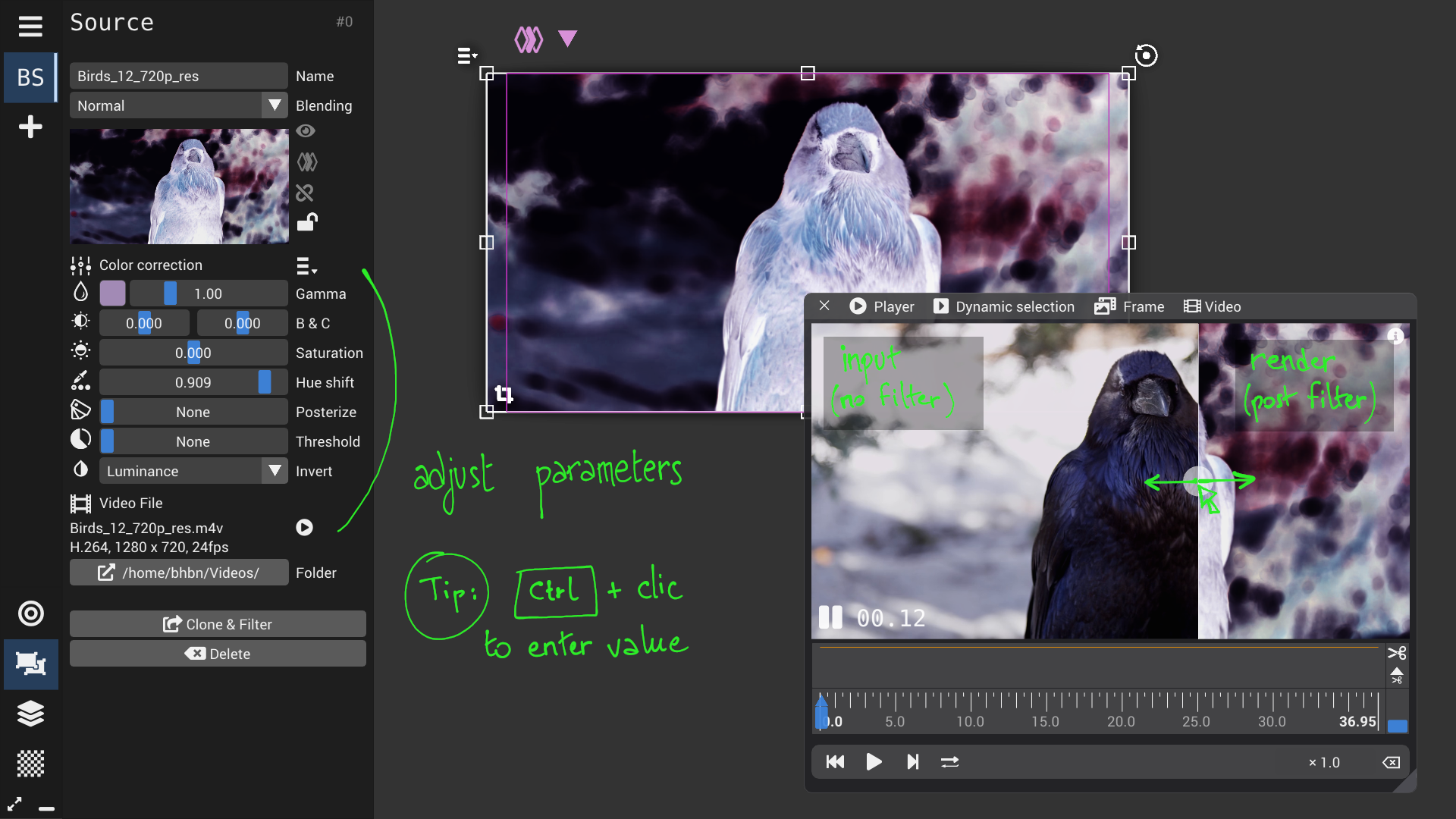
Source configuration panel
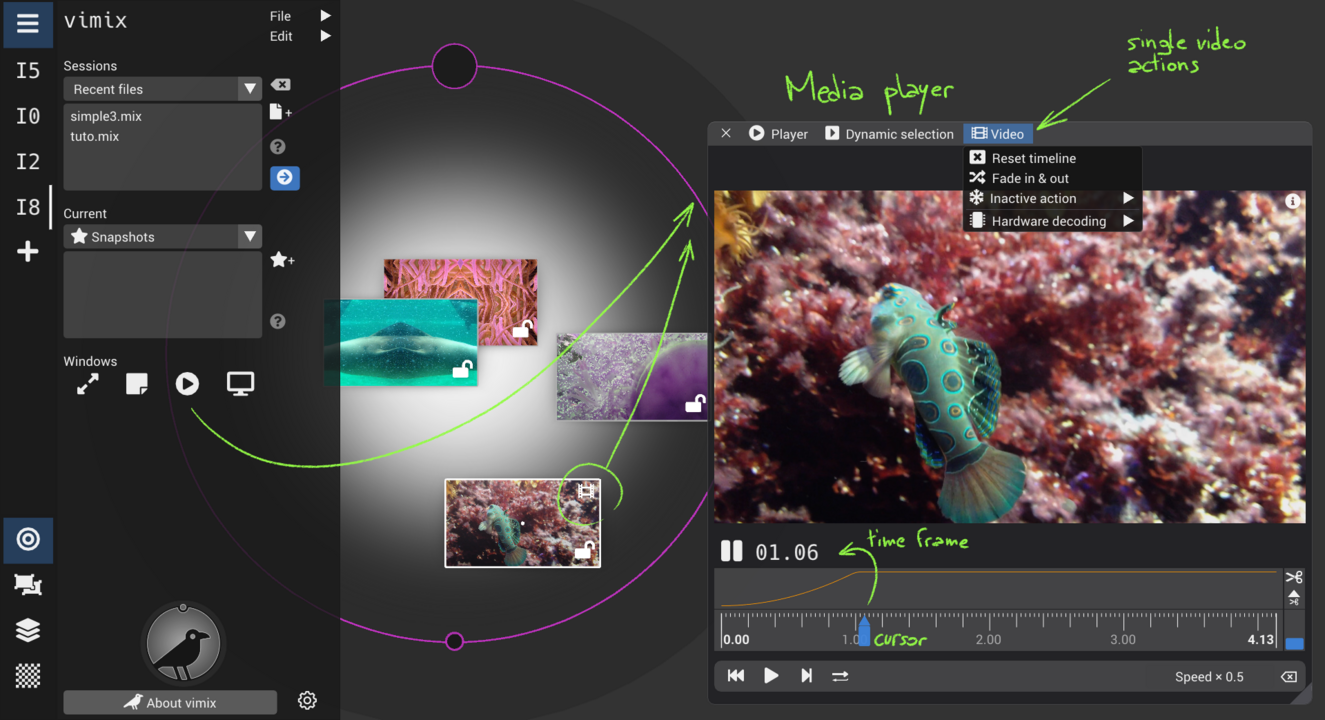
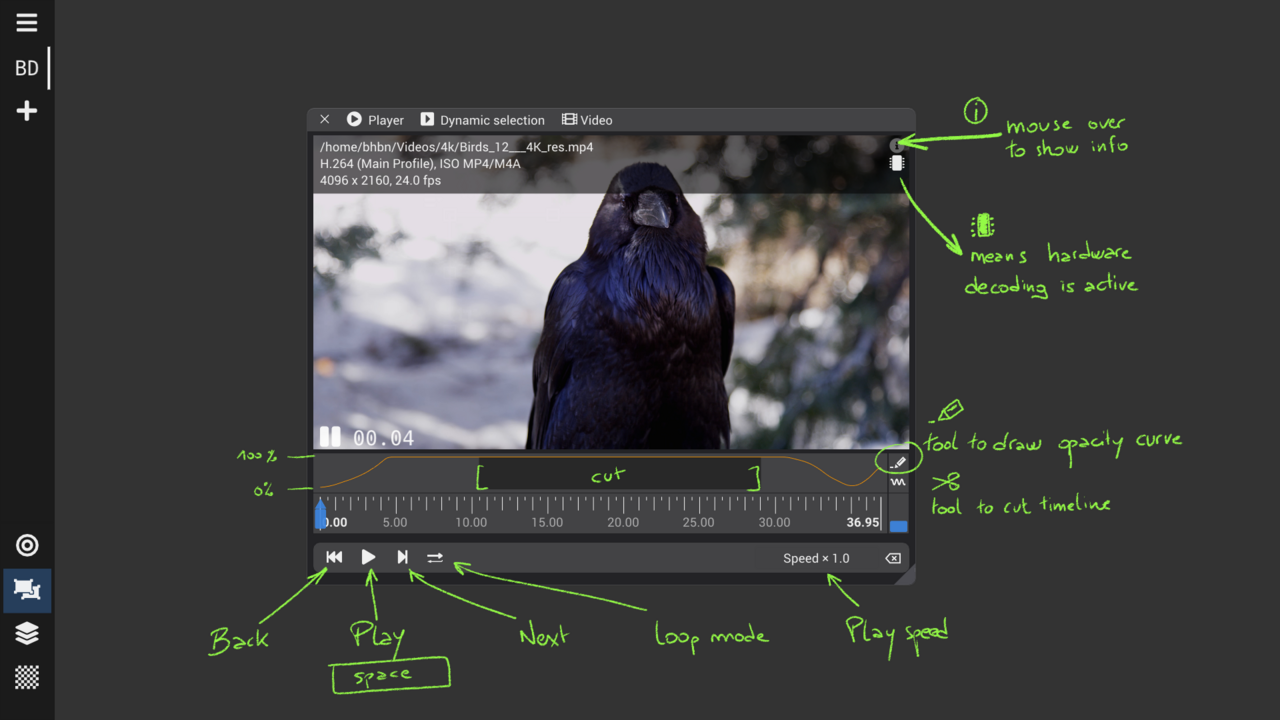
Media player : control playback of media
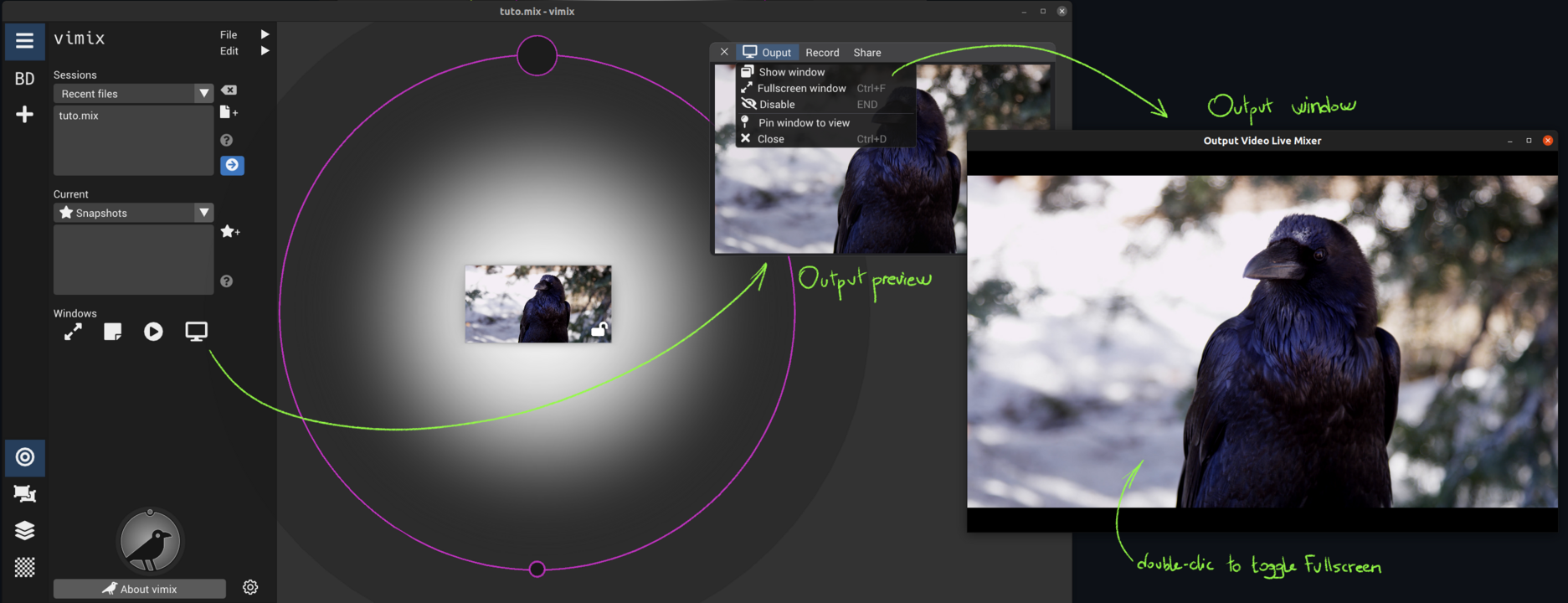
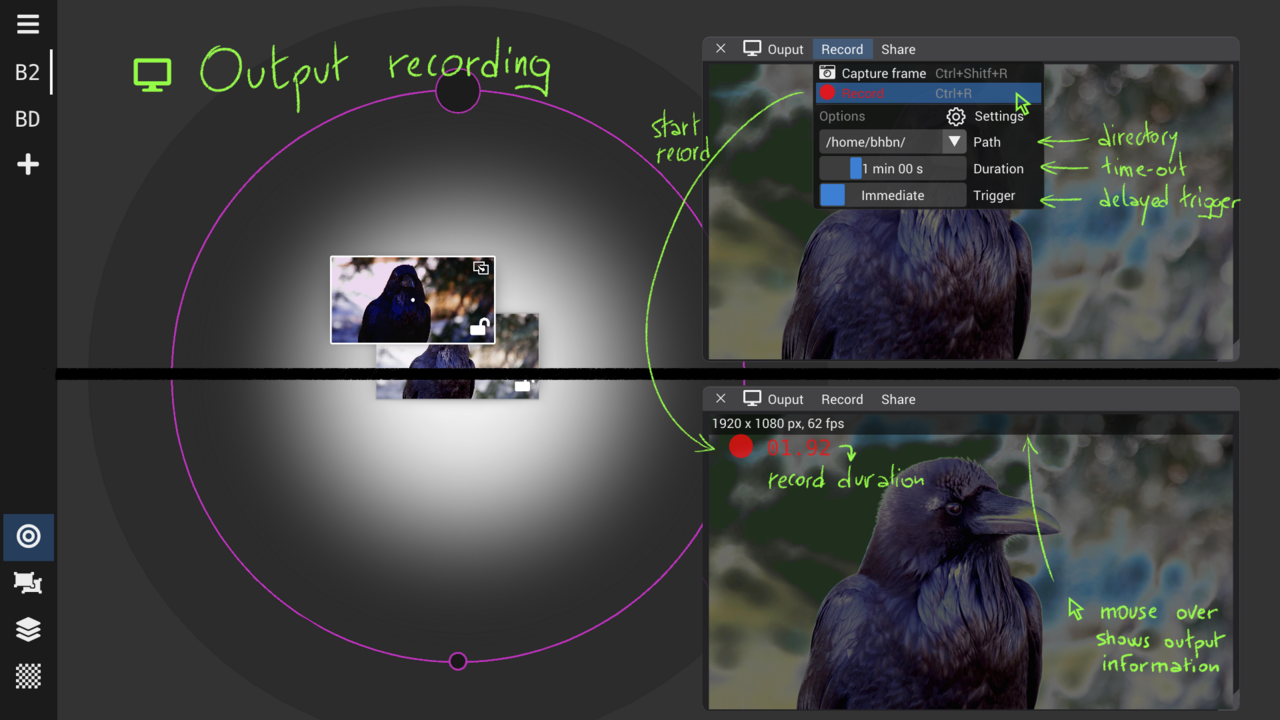
Record output stream
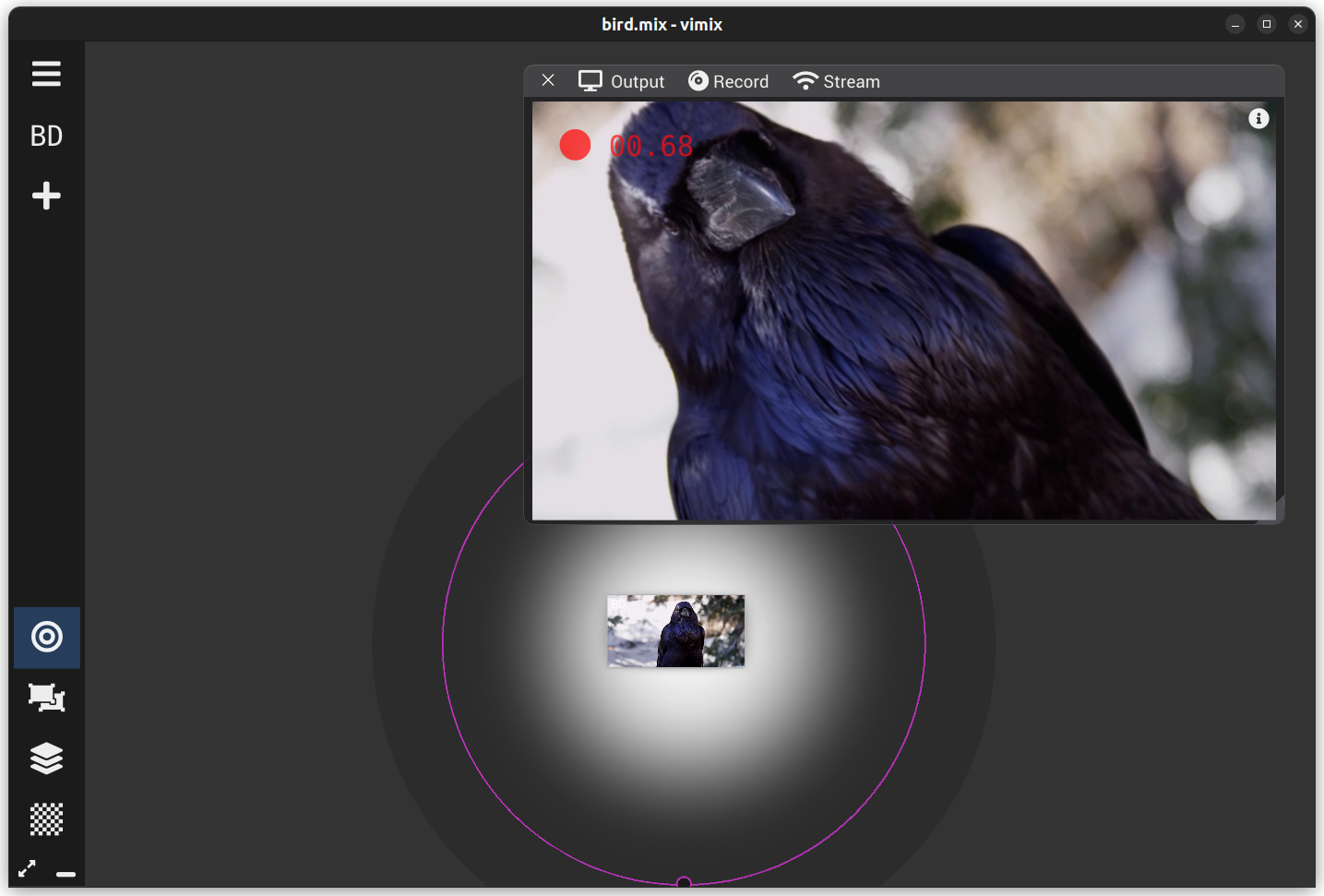
Recording of vimix output generates a video file from the live mix. It is triggered and controlled from the Record menu of the Output window.
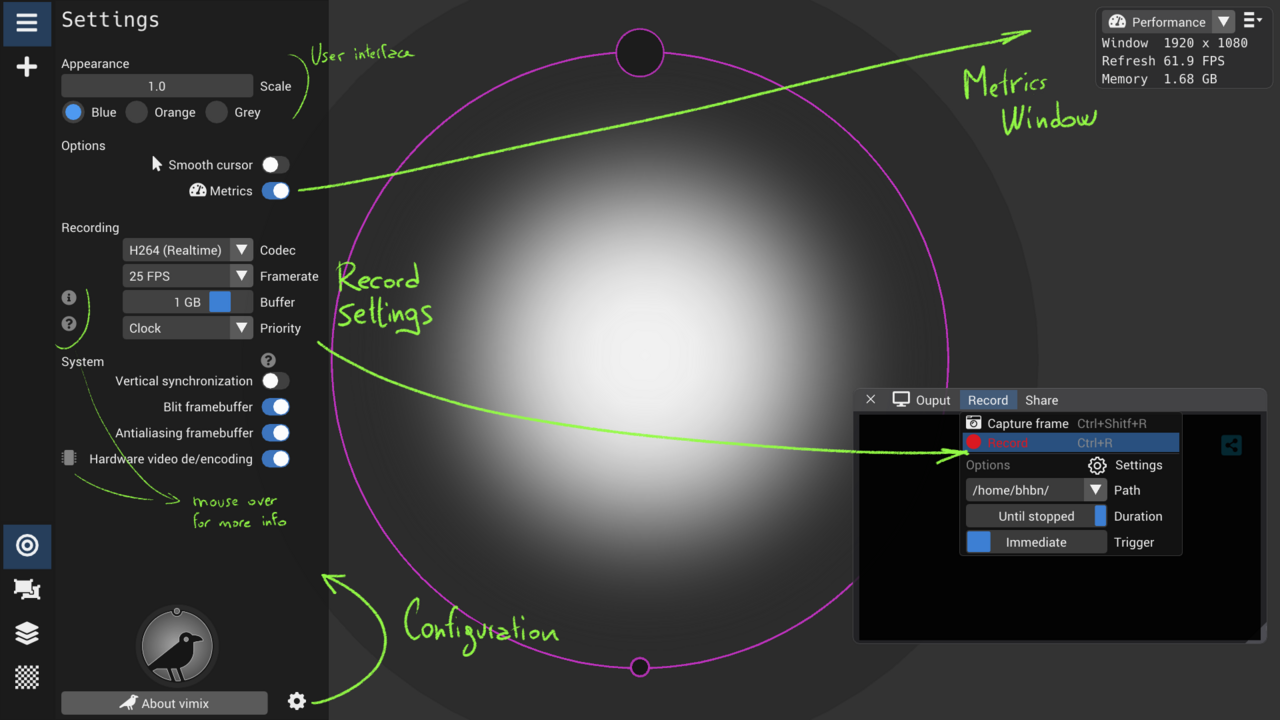
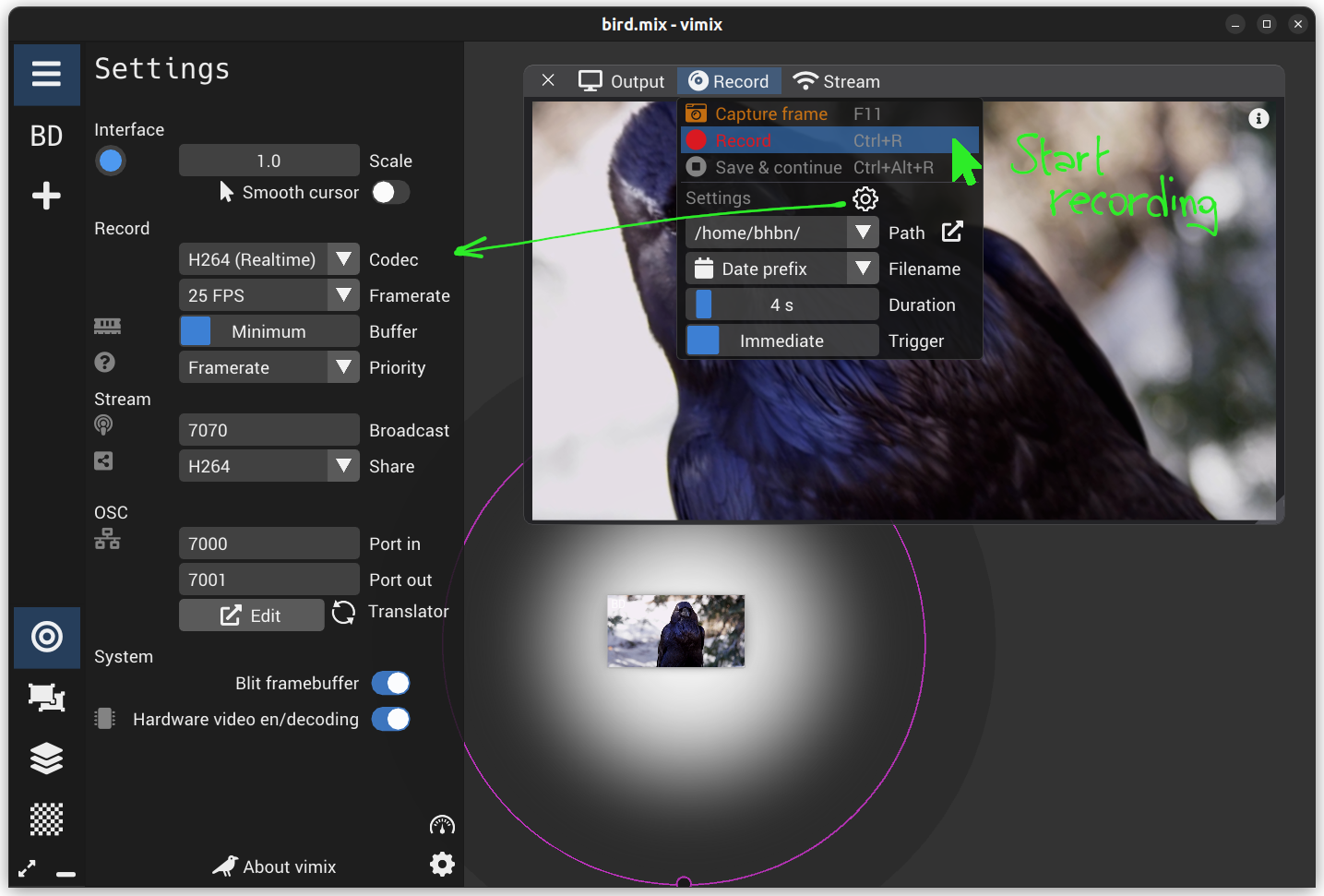
The options of recording are;
Path: Folder where the video file will be stored.Filename: Video file name can either be the session filename prefixed by date and time, or the session filename followed by a number.Duration: How long to record, from 1 second to 'Until stopped'.Trigger: Start recording after a few seconds (to get ready) or immediately.
Video recording live is a GPU and CPU intensive process (image capture, color conversion, encoding in video codec, saving to hard-drive). The recording Settings allow you to adjust to your hardware capabilities;
Codec: Video file internal format; this affects quality and recording speed. H264 are the fastest (and GPU accelerated). Others offer a better image quality preservation but are slower.Framerate: Frame rate of the video; 15, 25 or 30 FPS (the higher, the more to encode).Buffer: How much RAM you wish to allocate for the recording buffer: large buffer allows storing in RAM some seconds of rendering to give time for the computer to encode the video in the background (after recording stopped).Priority: If the buffer gets full, it can happen that the recording gets delayed from the real time; vimix can either give priority to maintain a constant framerate in the produced video (the duration is altered), or to ensure frame timestamps and duration are correct (the framerate is altered).
During recording, all normal operations in vimix are possible. The output window shows the indication of recording duration.
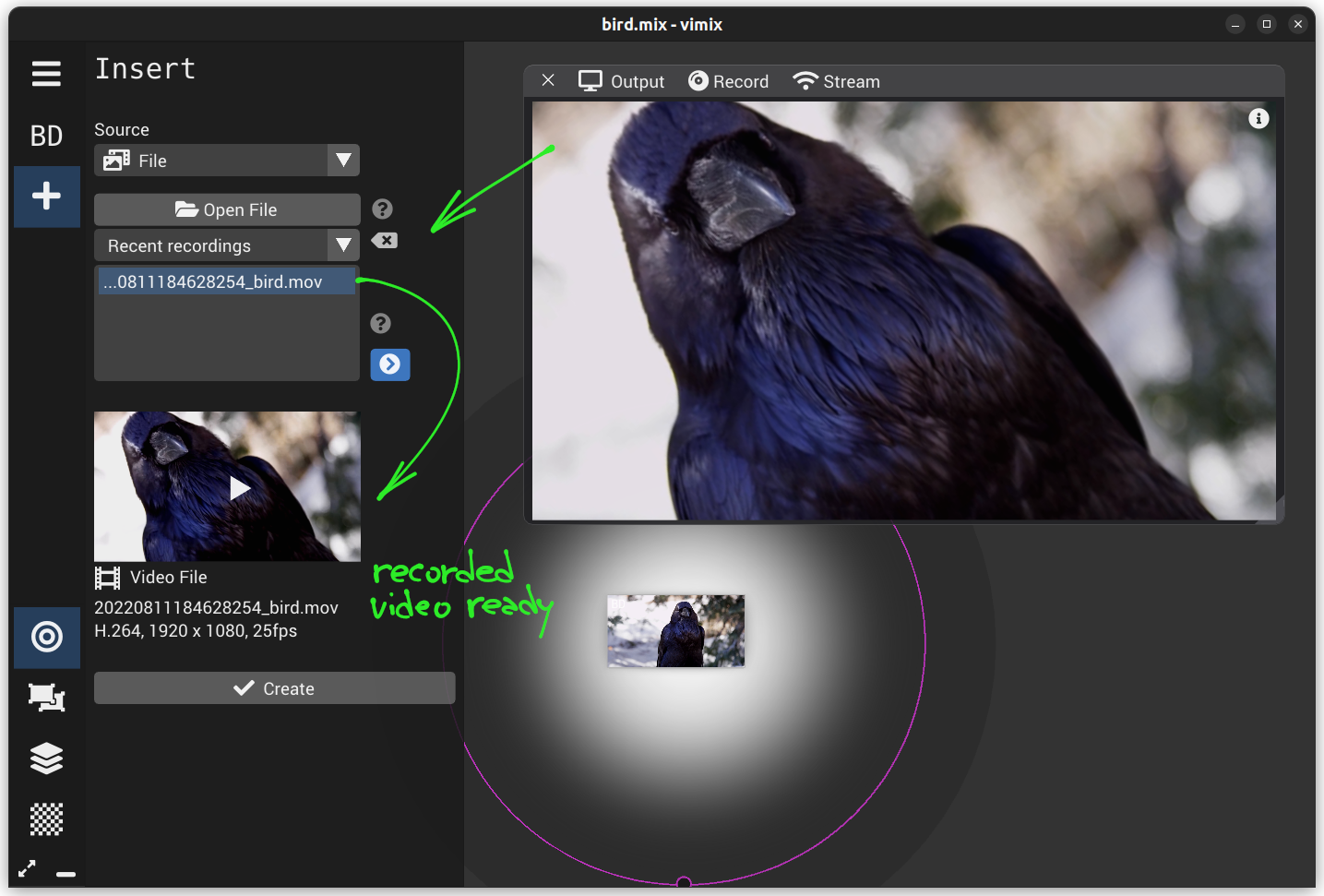
After recording, you can immediately re-inject the produced video into vimix.
Insert a source with +; the source type File with the list of Recent recordings appears by default after a new recording (i.e. the auto-preload option is enabled)
Help and guides
Open Sound Control
About vimix